The future of autonomous vehicles depends not only on the capabilities of the technology but also on the industry’s commitment to safety and the public’s trust in its potential to improve our lives.
As the development and deployment of self-driving vehicles continues to accelerate, so do the concerns surrounding their safety. Autonomous technology promises to revolutionize transportation, but it also poses significant risks.
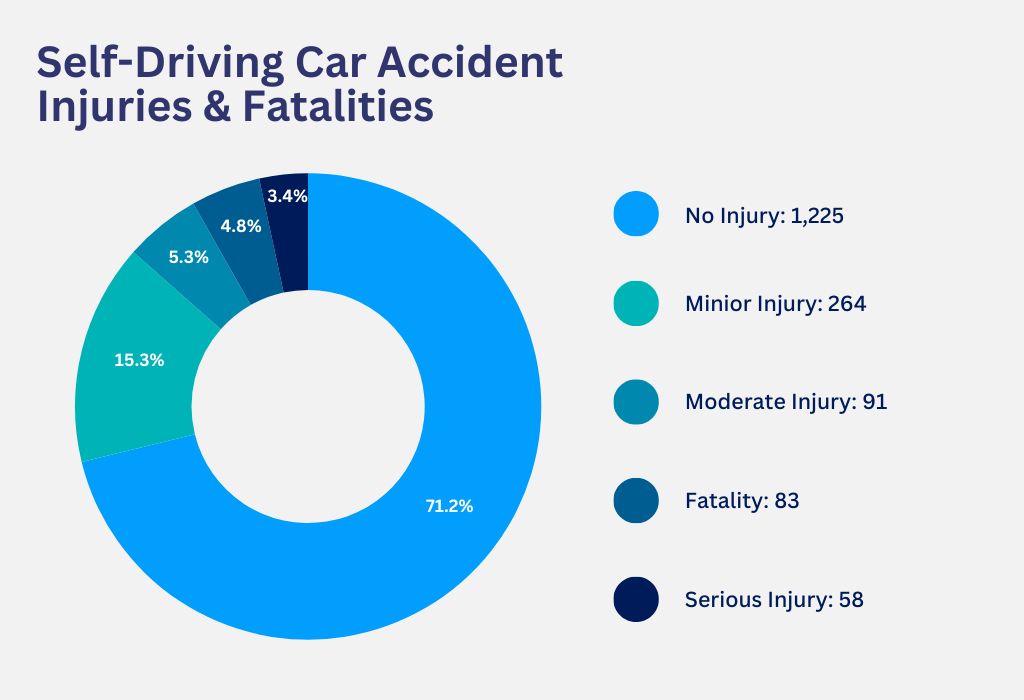
Based on a recent analysis of self-driving car accidents, 83 fatalities have been linked to autonomous vehicles. This raises questions about the reliability and safety of these vehicles, so let’s take a closer look at the data and the broader implications of self-driving car deaths.
The Data: Self-Driving Car Incidents and Fatalities
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) began officially collecting incident reports from autonomous vehicle companies in June 2021. Since then, there have been 3,979 reported incidents involving vehicles equipped with Automated Driving Systems (ADS) or Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS).
Of these incidents, 83 have resulted in fatalities. This data underscores the dangers of autonomous vehicles, particularly as they become more prevalent on our roads.
Deaths From Tesla Accidents
The first known fatal crash involving Tesla’s Autopilot system occurred in January 2016 in China’s Hubei province. The vehicle, a Tesla Model S, failed to take necessary action and crashed, killing the driver. Initially, Tesla stated that the car was too badly damaged to determine whether Autopilot was engaged at the time. However, the fact that the vehicle did not attempt to avoid the collision raises serious concerns about the effectiveness of the system.
In May 2016, another fatal Autopilot crash occurred in Florida. A Tesla Model S, while on Autopilot, failed to recognize the white side of a tractor-trailer against a brightly lit sky and crashed into it, killing the driver. In a subsequent civil suit, Tesla documented that the car had indeed been on Autopilot at the time of the crash.
Yet again, another tragic incident occurred in Texas in 2019, when Walter Huang engaged the autopilot feature of his Tesla Model X. The car veered out of its lane and accelerated, ultimately crashing into a barrier at 70 mph, killing Huang. Tesla later settled a wrongful death lawsuit with Huang’s family for an undisclosed amount. This case brought to light the dangers of over-reliance on Tesla’s autopilot system and the potential consequences when drivers do not remain attentive.
There has been confusion and litigation surrounding Tesla’s Autopilot and Full Self-Driving systems, which despite their names, are classified as ADAS, not the more advanced systems (ADS). The incidents highlighted above are only a few of the fatal accidents involving Tesla cars.
Other Self-Driving Car Companies with Fatal Accidents
In March 2018, the first recorded pedestrian fatality involving a fully autonomous vehicle occurred in Tempe, Arizona. An Uber test vehicle struck and killed Elaine Herzberg as she crossed the street. The vehicle was in self-driving mode at the time, with a backup driver behind the wheel. This incident sent shockwaves through the industry, highlighting the potential for catastrophic failures in autonomous systems. The backup driver was later charged with negligent homicide, setting a precedent for the legal responsibilities that come with operating these vehicles.
Then in October 2023, a pedestrian in San Francisco was struck by a hit-and-run driver and thrown into the path of a Cruise robotaxi. The self-driving car then drove over her, resulting in her death. This incident is particularly concerning given the growing presence of robotaxis in urban areas. It raises questions about the ability of autonomous vehicles to react appropriately in complex, real-world scenarios. It’s unclear whether the world is ready for self-driving taxis yet.
Implications: Reputation and Regulations
These high-profile accidents have significantly impacted public perception of autonomous vehicles. While self-driving technology holds great promise, each death raises doubts about its safety and reliability. Companies like Tesla, Uber, and Cruise face increasing scrutiny, and public trust in their technology has been shaken. These incidents may also slow the adoption of autonomous vehicles as potential users become more hesitant to embrace this emerging technology.
In response to these incidents, stricter guidelines and oversight on autonomous vehicles are being imposed. Both federal and state governments are working to establish clear regulations to ensure the safety of these vehicles on public roads. Liability and insurance issues also come into play, as determining fault in accidents involving autonomous vehicles can be complex. As the technology continues to evolve, so too will the legal frameworks governing its use.
Safety Measures and Technological Improvements
In light of these fatalities, companies developing autonomous vehicles have been working to enhance safety protocols and improve their technology. Advances in sensor technology, machine learning algorithms, and real-time data processing are being implemented to reduce the likelihood of accidents. However, the responsibility also lies with the companies to ensure that these vehicles are tested rigorously and that drivers are adequately informed about the limitations of the systems they are using.
The rise of autonomous vehicles marks a significant milestone in transportation innovation. However, the fatalities associated with self-driving cars serve as a stark reminder that with innovation comes risk. As we move forward, it is crucial to balance the pursuit of technological advancement with the need to protect human life. The future of autonomous vehicles depends not only on the capabilities of the technology but also on the industry’s commitment to safety and the public’s trust in its potential to improve our lives.


Join the conversation!